The goal of classical education is to cultivate lifelong learners who possess the skills, knowledge, and wisdom to become engaged citizens and leaders in their communities.
Classical education is an approach to education that is rooted in the ancient Greek and Roman educational traditions. It is based on the belief that the study of grammar, logic, rhetoric within the framework of mathematics, history, and the sciences, provides the best foundation for intellectual and moral development. Classical education emphasizes the importance of critical thinking, logic, and the ability to communicate effectively in both oral and written forms. It also focuses on the study of classical literature, philosophy, and history as a means of understanding the human condition and the enduring questions of life. Classical education is often structured around the trivium, 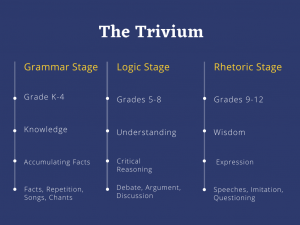 which is a three-part system of learning that includes grammar, logic, and rhetoric, and the quadrivium, which includes arithmetic, geometry, music, and astronomy. These subjects were considered essential for a well-rounded education in ancient Greece and Rome, and were studied after the mastery of the trivium. The quadrivium was seen as a higher level of learning that allowed students to explore the natural world and understand its underlying mathematical principles. Arithmetic and geometry were studied as foundational subjects for all other sciences, music was seen as a way to understand the mathematical relationships between sounds and rhythms, and astronomy was studied as a way to understand the movements of the heavens and their relationship to the earth.
which is a three-part system of learning that includes grammar, logic, and rhetoric, and the quadrivium, which includes arithmetic, geometry, music, and astronomy. These subjects were considered essential for a well-rounded education in ancient Greece and Rome, and were studied after the mastery of the trivium. The quadrivium was seen as a higher level of learning that allowed students to explore the natural world and understand its underlying mathematical principles. Arithmetic and geometry were studied as foundational subjects for all other sciences, music was seen as a way to understand the mathematical relationships between sounds and rhythms, and astronomy was studied as a way to understand the movements of the heavens and their relationship to the earth.
Origins of Logic
Aristotle’s logic is a system of reasoning that emphasizes the importance of clear and accurate thinking. It is based on the principles of deduction and syllogism, which involve using premises to draw conclusions. Aristotle believed that all valid arguments can be reduced to syllogisms, which consist of two premises and a conclusion. He also identified several categories of thought and developed a system of classification that is still used today. Aristotle’s logic emphasizes the importance of careful observation and analysis.
Syllogism is a form of logical reasoning in which a conclusion is drawn from two premises. The premises are statements or propositions that are assumed to be true, and the conclusion follows logically from them. Syllogisms are typically constructed using the format of “All A are B” and “All B are C,” and then concluding that “All A are C.” For example, “All (B) organisms are (A) important [major premise], an (C) elephant is a type of (B) organisms [minor premise], therefore(C) elephants are important (A) [conclusion]” is a syllogism. Syllogisms are an important tool in deductive reasoning and are widely used in philosophy, mathematics, and other fields that require logical analysis.

